(The platform has authorized to do further research and development in the affiliated company, T-E Meds, Inc.)
T-E Meds website: https://www.temeds.com/
Based on our propriety "multi-arm linker" and "drug bundle" platforms, T-E Meds establishes two types of antibody drug conjugate (ADC) drug candidates, which are designed as the scFv-based ADC and IgG-based ADC.
scFv-based ADC
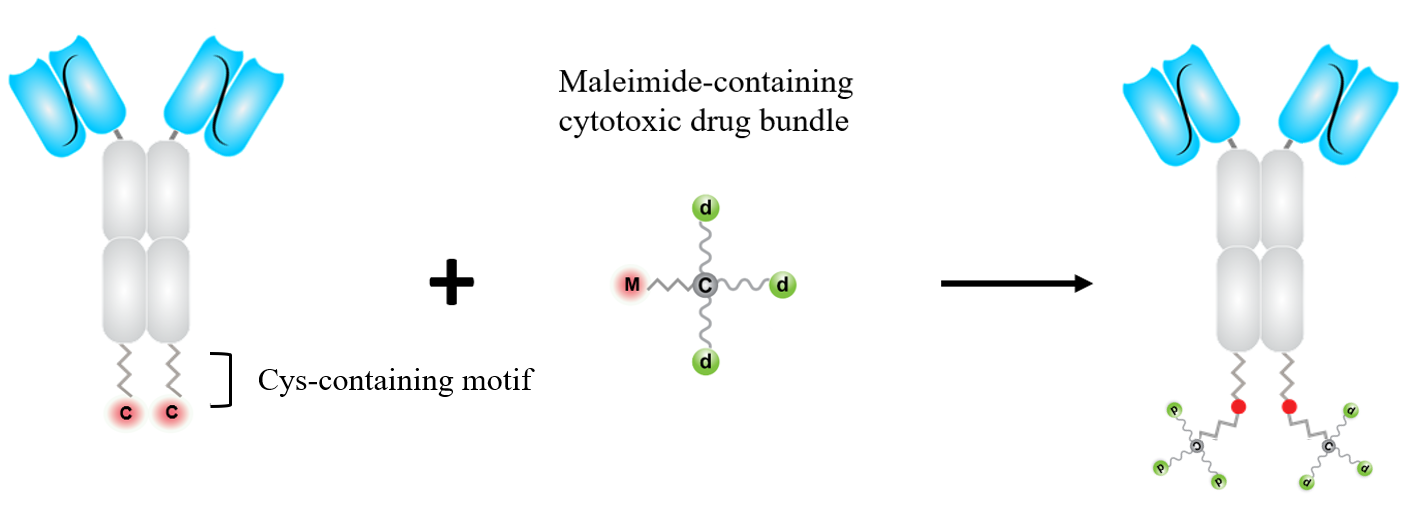
The cytotoxic drug bundles are conjugated to antibody molecules to form ADCs. In our preferred constructs, the Fab part of the antibody molecule is reconfigured to single-chain variable fragment (scFv), so that the antibody molecule is presented as two “extended heavy chains” covalently associated by interchain disulfide bonds.
For each heavy chain, the N-terminal is scFv, the center part is CH2-CH3 domains of immunoglobulin g1 chain, and at the C-terminal is a short peptide linker. The complexing of Zn2+ with the cysteine residue and the adjacent amino acids enhances the SH group as a nucleophile.
The conjugation of the cytotoxic drug bundles is thus made via a site-specific SH-maleimide "Michael Reaction" to the cysteine residues at the C-termini of the heavy chains. Two drug bundles are conjugated per antibody molecule. The ADC product is homogeneous with a finite DAR of 6, 8, or 10, using drug bundles carrying 3, 4, or 5 cytotoxic drug molecules.
An emerging consensus in the ADC field is that if an antibody drug conjugate maintains soluble and stable, higher DAR is more efficacious.
Here shows the preparation process of a scFv-based ADC.
IgG-based ADC
T-E Meds possesses an innovative "drug bundle" technology that facilitates the packaging of multiple drug molecules, whether of the same or different types, into a bundled configuration equipped with a click chemistry functional group, such as DBCO.
These drug bundles, predominantly synthesized through solid-phase peptide synthesis, comprise hydrophilic ammino acids and PEGylated amino acids, with varying ethylene glycol unit counts, allowing for tailored hydrophilicity.
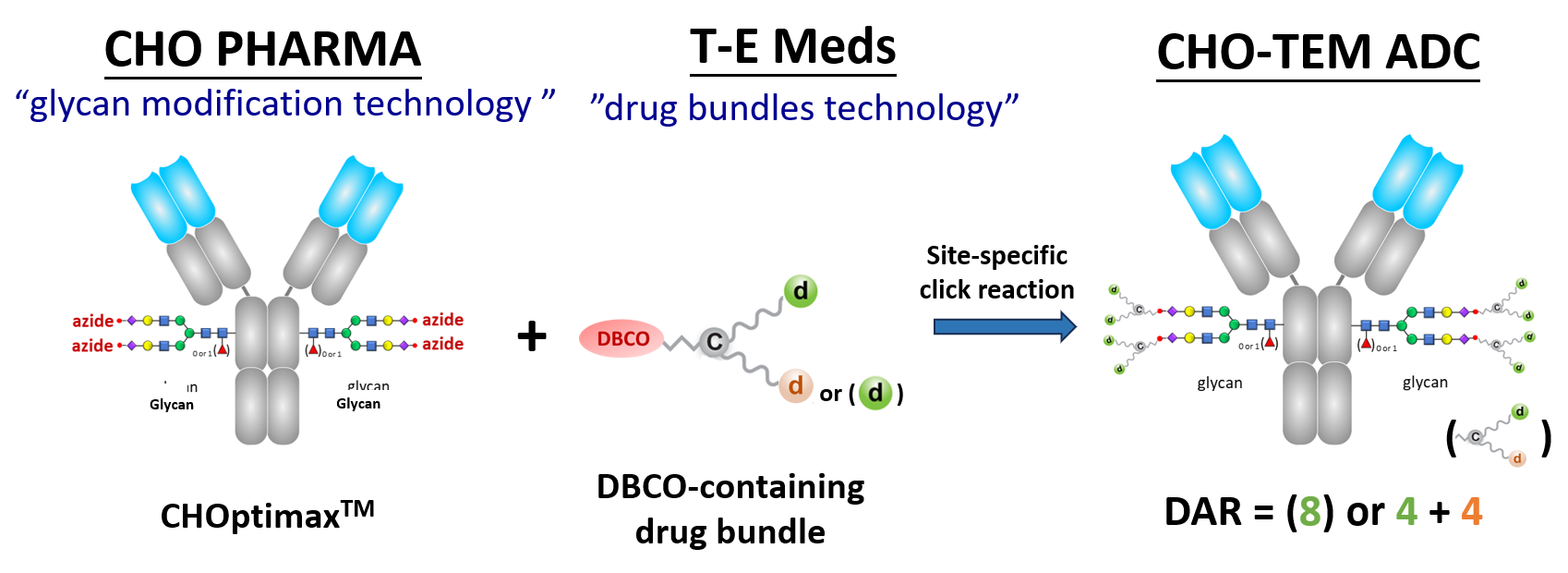
We are thrilled to establish a strategic business alliance with CHO Pharma Inc., the collaboration aims to leverage our complementary technologies in the development of novel CHO-TEM ADC products.
CHO Pharma has a unique "glucan modification" technology for precise alteration the glycan structure of IgG Fc. This process requires only one glycosyltransferase for cleaving off carbohygrate chains, leaving behind a monosaccharide (with or without fucose), and then ligating a prepared oligosaccharide.
Notably, the oligosaccharide consists of 11 linked monosaccharides, including two branching stretches of 5-member oligosaccharides, with the terminal sialic acid already conjugated with an azido group.
When mixed in an aqueous solution without the need for organic solvents, the drug bundles and glycan-modified antibodies exhibit rapid reactivity, achieving a conjugation rate exceeding 95%.
The resulting ADC products boast a high Drug-to Antibody (DAR) of 8, consisting of eight drug molecules of the same type or four each of two different types. These ADCs have demonstrated the excellent efficacy in killing tumor cells in vivo cytotoxicity experiments and exhibited stability, with no drug molecule or drug bundle shedding observed in human serum and plasma in vitro.
In summary, CHO-TEM ADC technology surpasses other ADC technologies, including those by Synaffix, in producing ADC candidates with higher DAR using a simplified process.
Here is an example of the CHO-TEM ADC technology.